The modern meaning of the term is especially focused in Graphical User Interface automation with the mission of cost and time saving.
RPA is mostly used in such business environments where IT systems run mission critical processes, where IT systems maintenance cost is high and where there’s a need of innovation in processes but no comprehensive digital transformation plan is present.
This article will detail the need and benefits of using code to develop software robots instead of trusting code-less tools proposed by new software vendors.
Some statistics
- Percentage of failed RPA implementations 50%
- Real average RPA cost reduction 15%
- Coded RPA VS code-less RPA error rate 5%
Key benefits
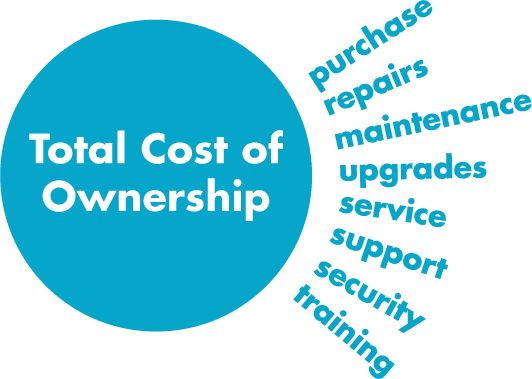
TCO reduction
Code-less RPA tools are advertised as easy to use and easy to produce quick wins. But are they really cost-effective solutions? Let’s take into account some TCO key points to discover how coded approach wins in the long term.
- Purchase.
- Learning.
- Manteinance.
- Upgrade.
- Service. Continuos integration
- Support.
- Security.
Case studies
Concurrent system automation
My team and I have successfully developed and ran a system of robots that are recording call center contact attempts for the main Italian telephony operator. The robots are developed with a distributed logic in mind, they all take data from one centralized database and open browsers concurrently to write records on company web based systems.
The database provider is MongoDB who give the opportunity of being flexible with new requirements and helps continuous integration together with excellent querying times.
The programming language used is C# with LINQ support. .NET framework together with C# makes it perfect to build complex robots as the whole process is under control, with real debugging tools, unlimited expandability thanks to years of development and NuGet packages.
SAP - ERP reliable automation
Robotic Process Automation hype is at an all-time high, with an alphabet soup of providers and offerings. Industry watchers are declaring RPA a must-evaluate technology, and some are heralding the start of the next industrial age. Software providers on both ends of the automation/AI spectrum scramble to incorporate new capabilities and meet in the middle, Given all that, one fact is often lost – many RPA implementations actually fail.
A few companies are resetting their robotics programs. As one CIO said, “We crashed, burned and are now resurrecting!” Here’s what they are learning and doing.

